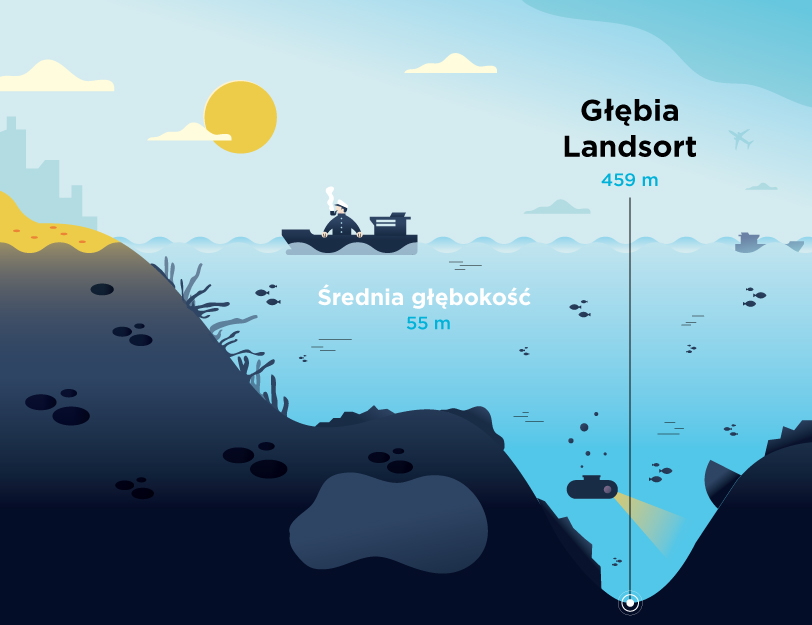
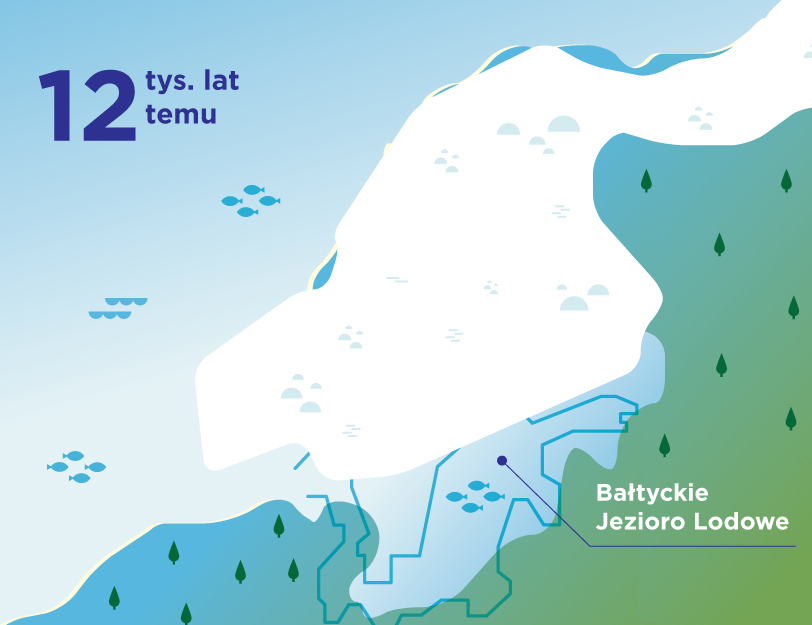
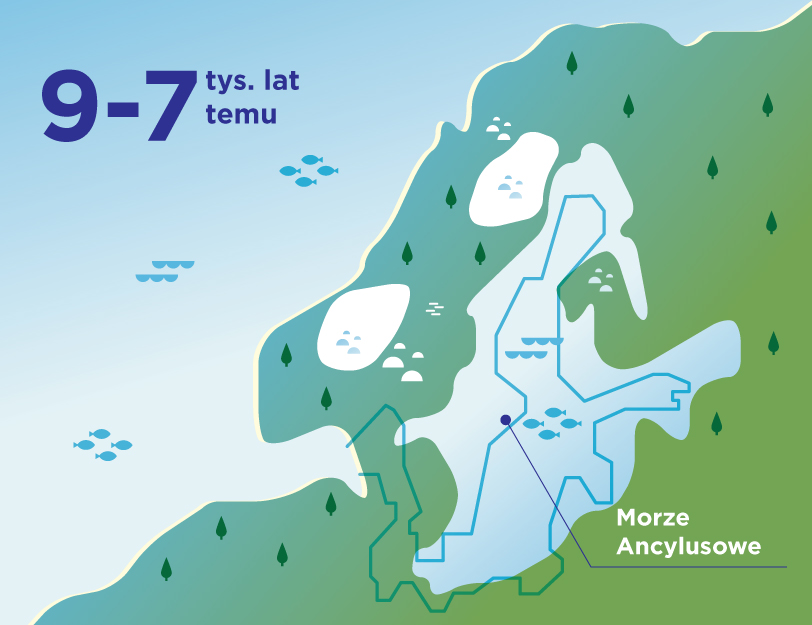
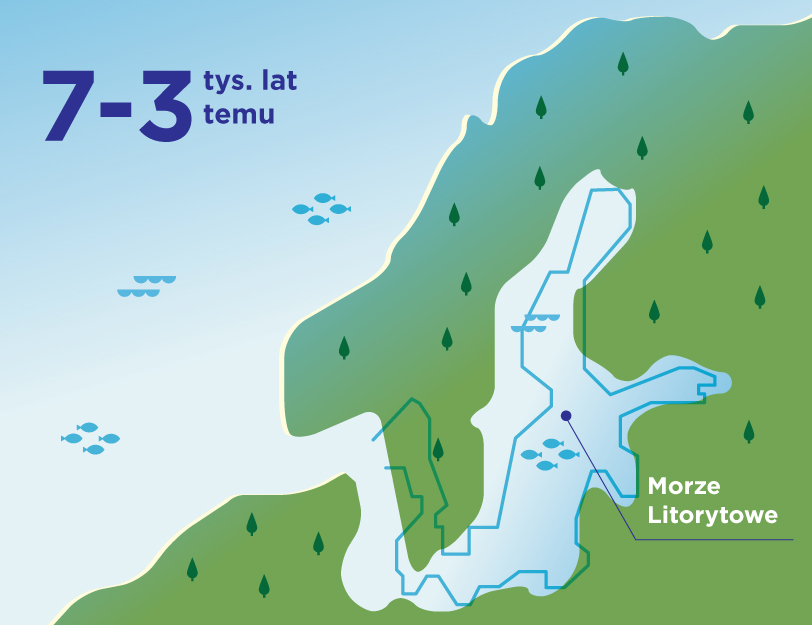
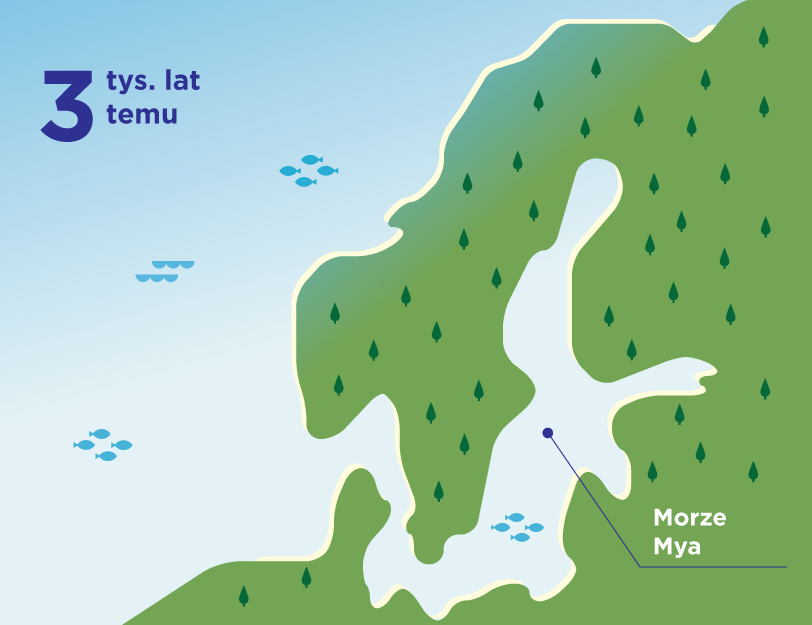
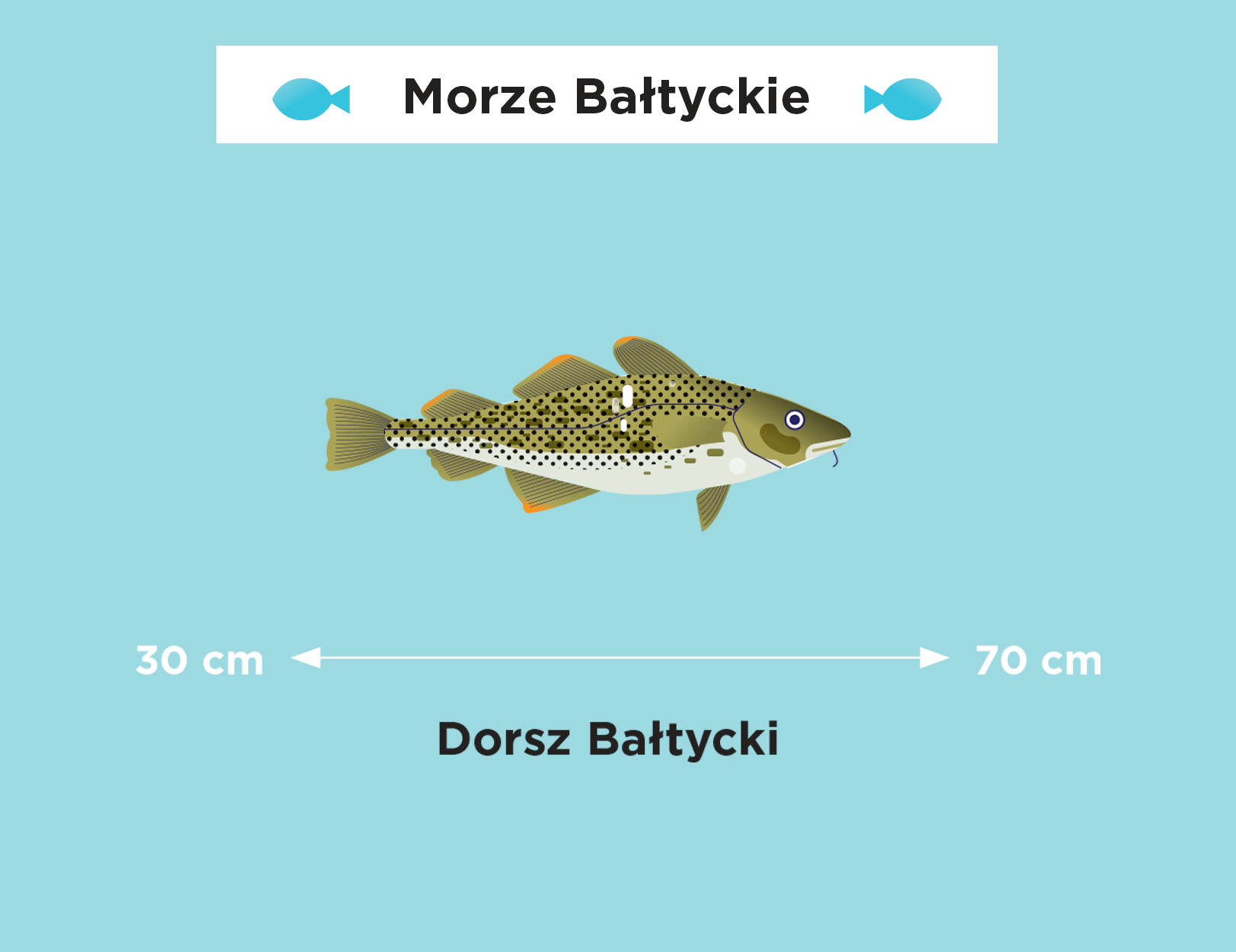
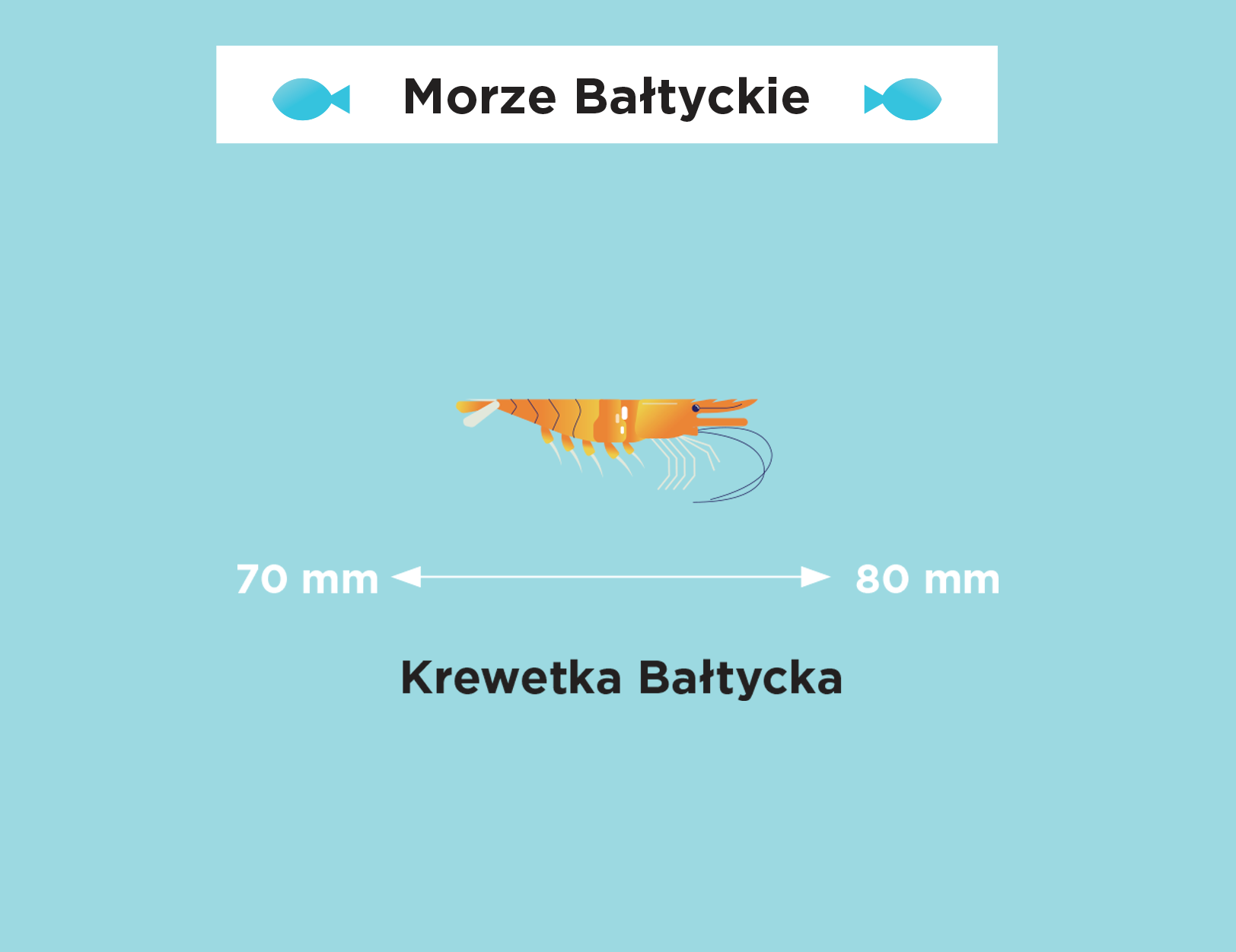
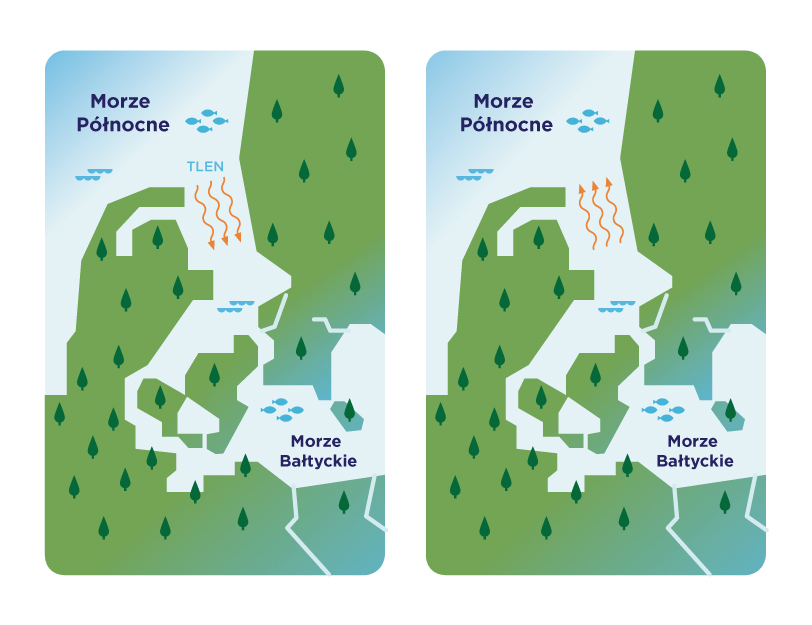
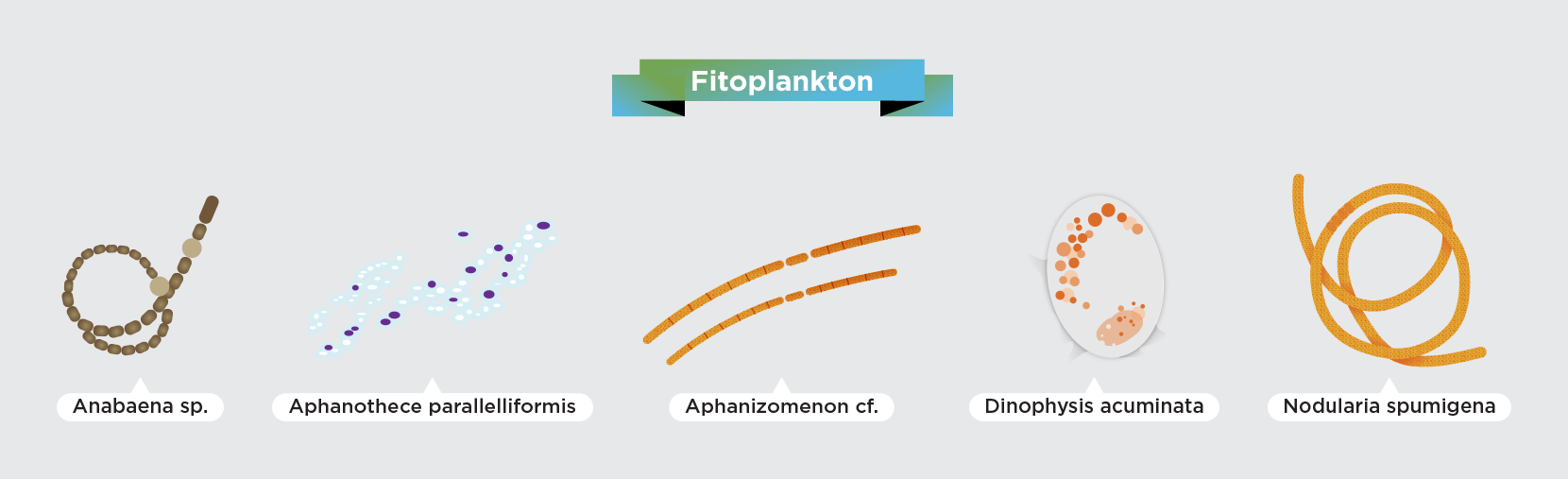
The Baltic Sea is extremely sensitive. Although it seems huge when we look at it from the beach, which may give us the impression that we have little influence on its waters, its shape, depth, coastline and low salinity make it easy to harm it. We can take care of the sea not only when we are on vacation, by being careful not to let garbage get into it, or by choosing natural creams with filters that will not harm its chemical composition when we swim.
We also take care of the Baltic Sea by protecting the purity of the rivers. We can go a step further, by making sure that the land we cultivate is not saturated with artificial fertilizers. They seep into the groundwater and end up in rivers, which then flow into the Baltic Sea. Sometimes even the fact that you spill floor cleaner in your yard and it soaks into your lawn can harm the Baltic Sea. Literally everything in the world is interconnected and affects each other. Please keep this in mind. So let's take care of the Baltic Sea, if we want to continue taking refreshing, although not too warm baths in it.
 English
English
 Polski
Polski
 Deutsch
Deutsch