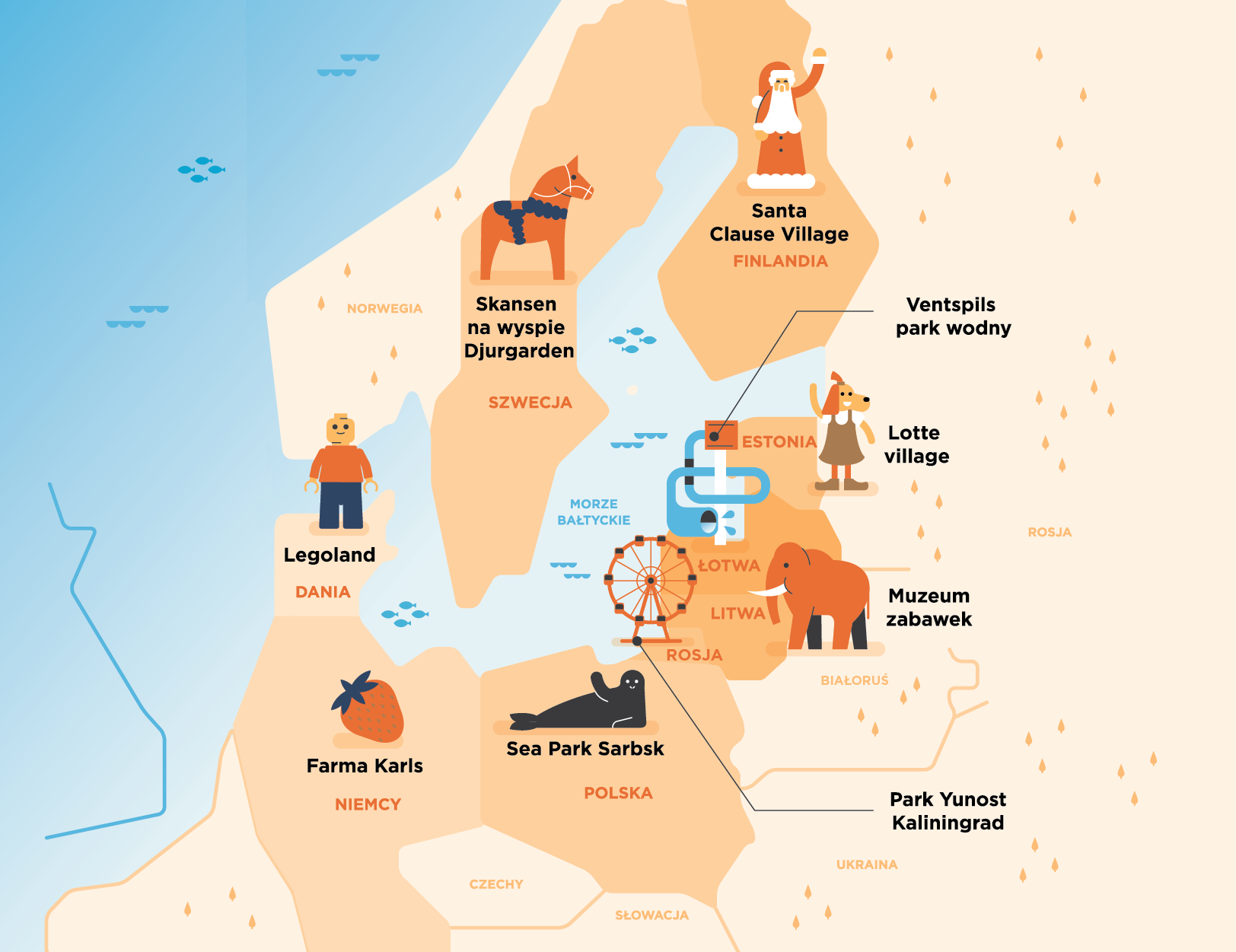
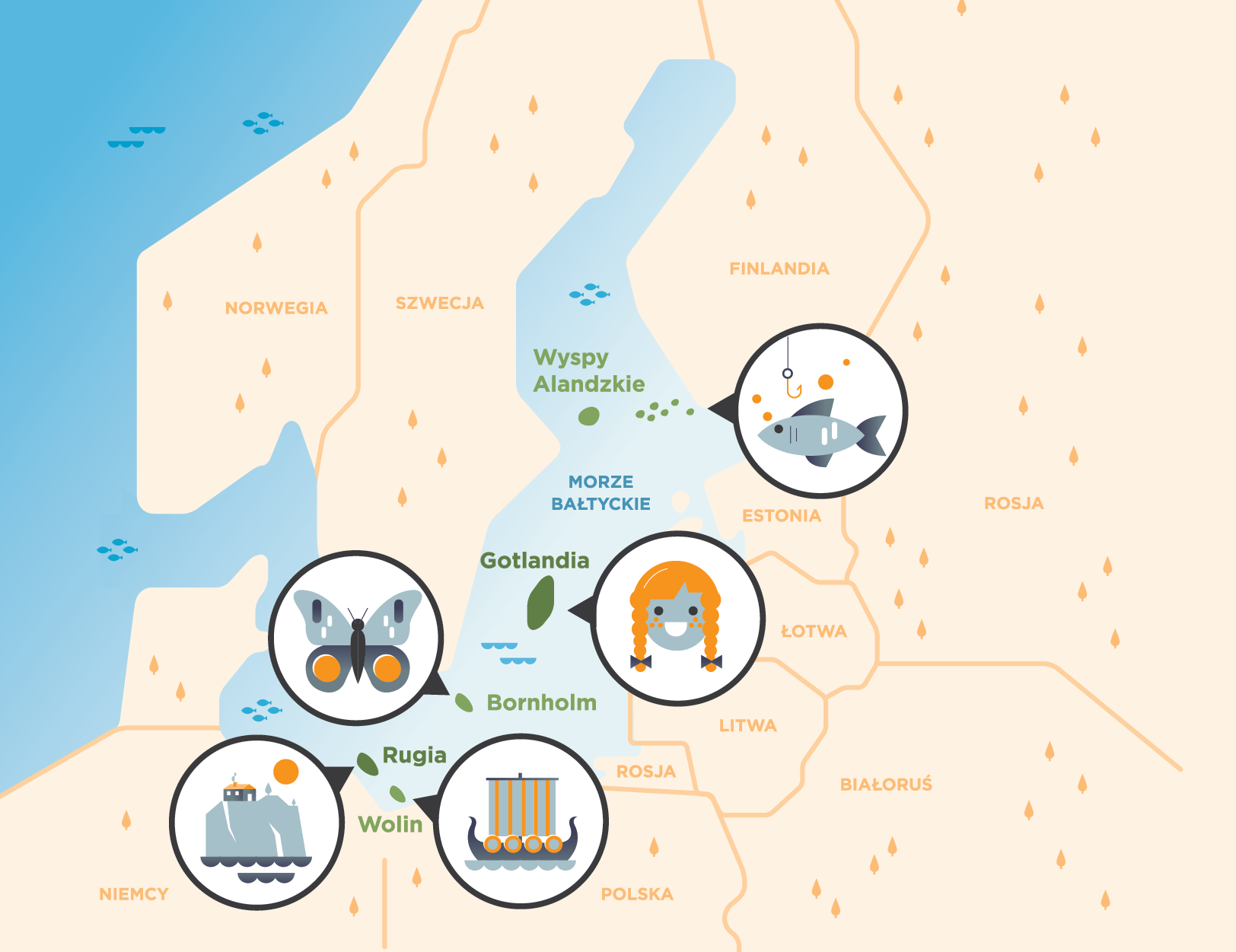
Welcome!
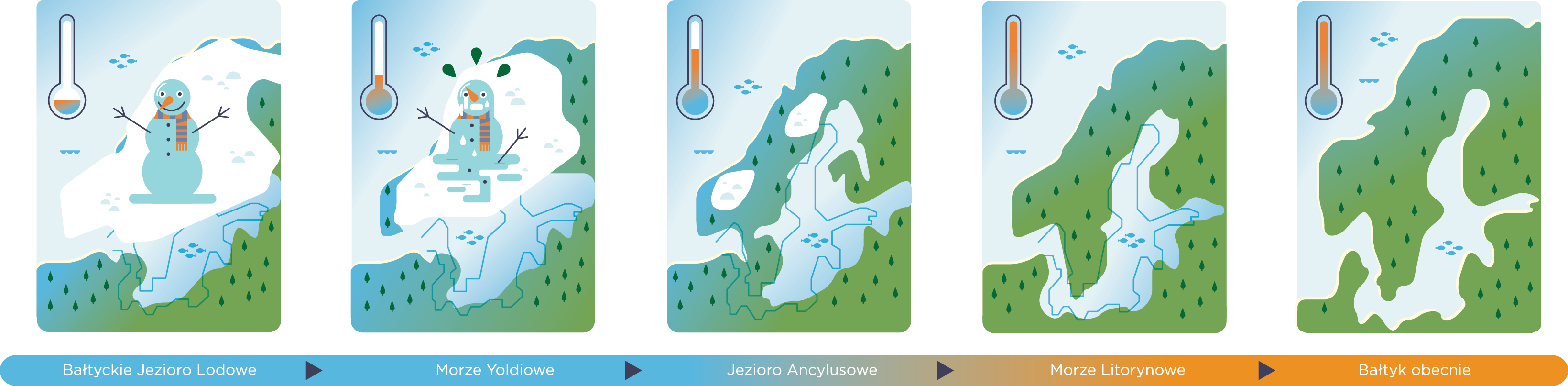
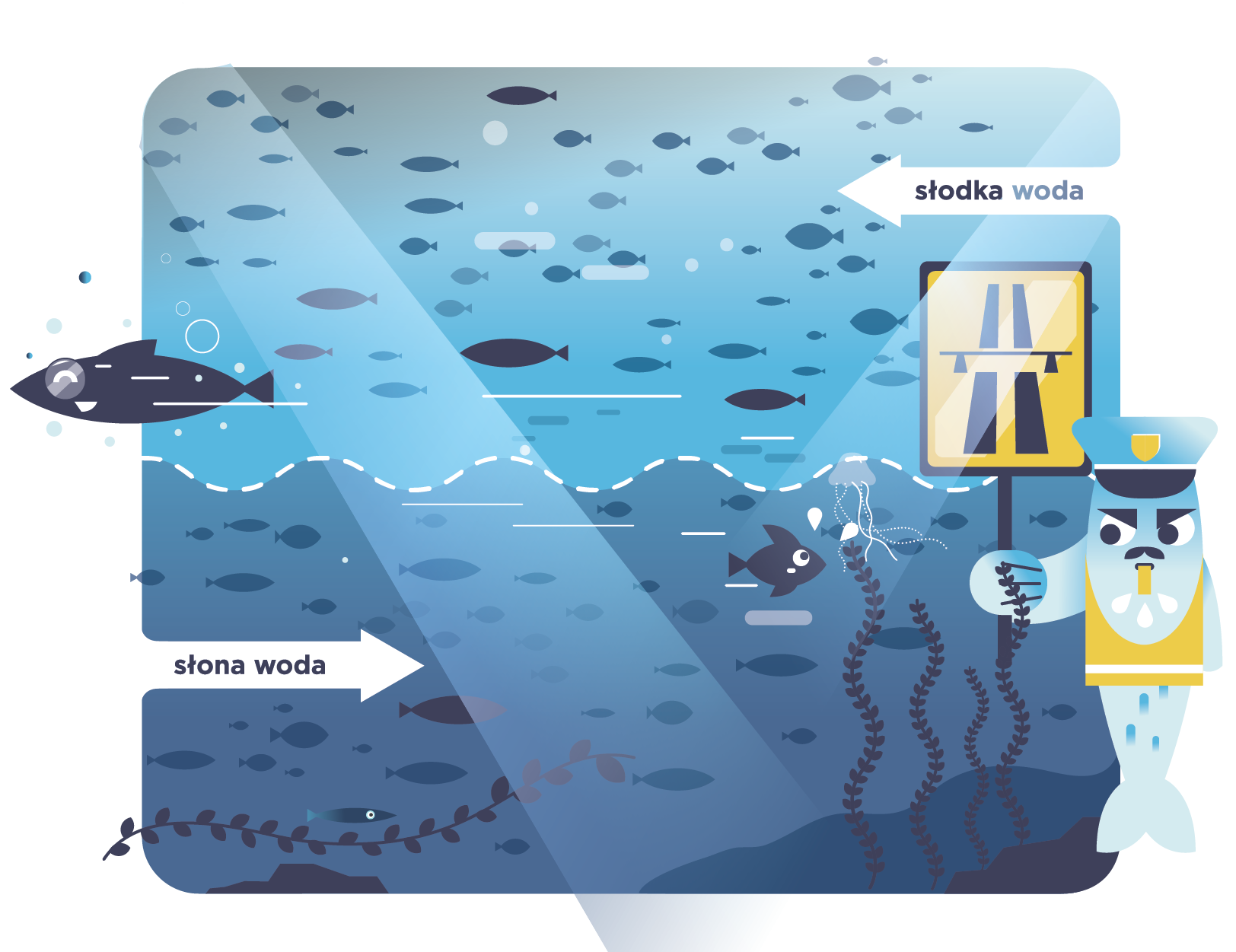
My name is Lagoon Cockle. You can find me at the seashore. I've been dropping in there on vacation for 14,000 years now with a fellow Baltic Clam and Blue Mussel. We are seashells. We used to be clam houses, just as snail shells act as their homes.
Since our residents have moved out, we spend our vacations on the Baltic coast. You may have heard about the fact that shells, when put to your ear, hum like the sea. That's because its history is recorded inside us.
 English
English
 Polski
Polski
 Deutsch
Deutsch